About Circular Knitting Machines
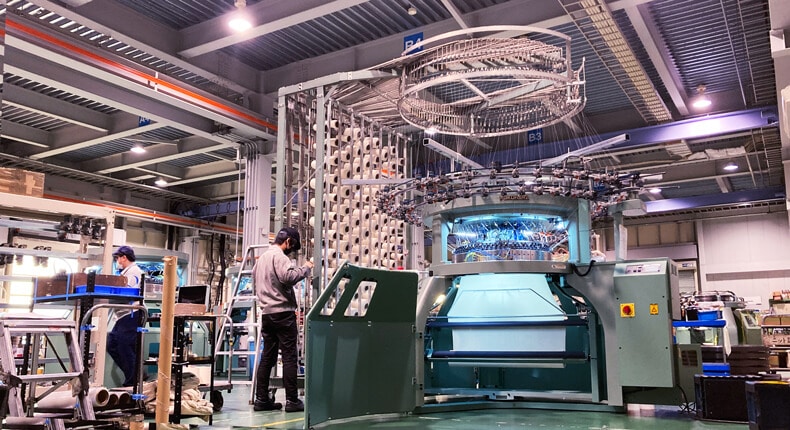

The “Maruamiki” is a circular knitting machine that we develop and produce. The name of this machine may be unfamiliar to many people, but it is actually very familiar to us. Everyone has at least one T-shirt or polo shirt. The machine that makes these fabrics (knitted fabrics) is the circular knitting machine.
Circular knitting machines are extremely productive and can produce large quantities of small knitted fabrics, making them ideal for mass production of cut and sewn products such as T-shirts and polo shirts.
Our company exports 95% of its products, but as the only manufacturer of circular knitting machines in Japan, our domestic share is almost 100%. Our circular knitting machines are exported to countries all over the world and are widely used, so you probably have products knitted on FUKUHARA circular knitting machines.
In this section, we will introduce the textile machine, the circular knitting machine, in more detail.
Contents
What are textiles (fabrics)?
Circular knitting machines are textile machines. So what is a textile?
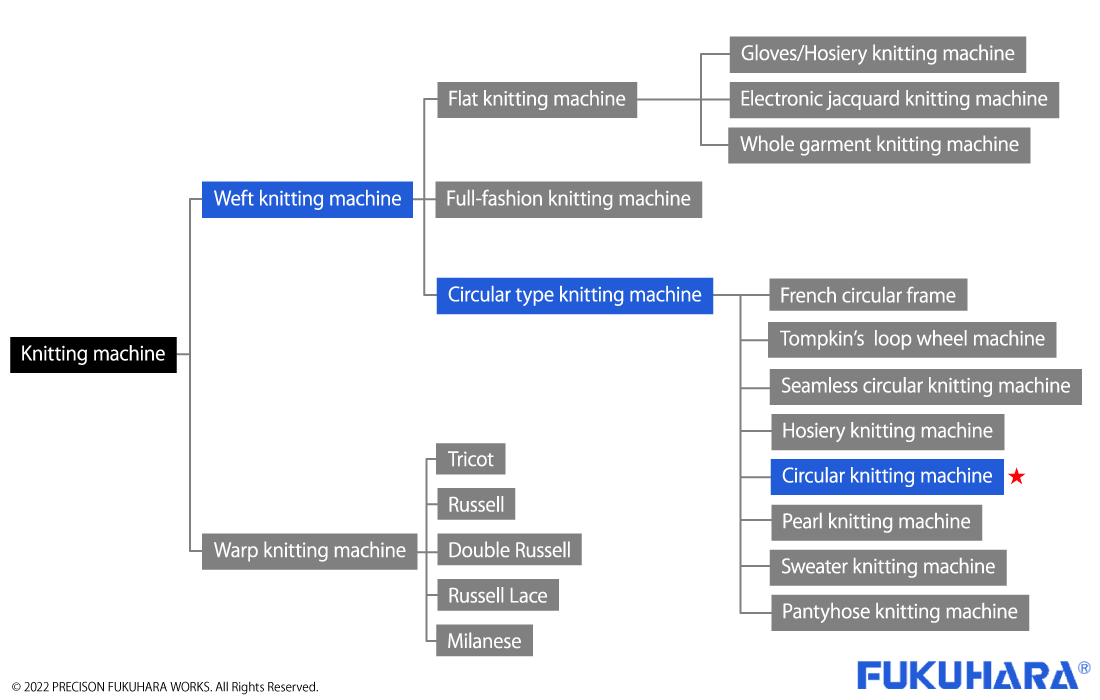
Textiles refer to the fabrics used to make clothes and other fabric products. There are three major types of textiles in the world: woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics, and knitted fabrics (hereafter knitted fabrics). Knitted fabrics are divided into warp and weft, and weft is further divided into weft knitting and circular knitting. Weft knitting is produced on a weft knitting machine, and circular knitting is produced on a circular knitting machine.
| Type | Features | Main Products |
|---|---|---|
|
Woven fabric 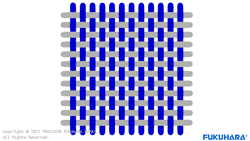
|
|
|
|
Non-woven (fabric) 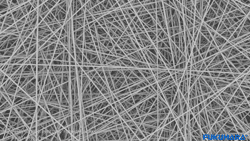
|
|
|
|
Knit 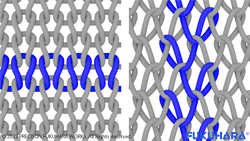
|
|
|
Classification of knitting machines
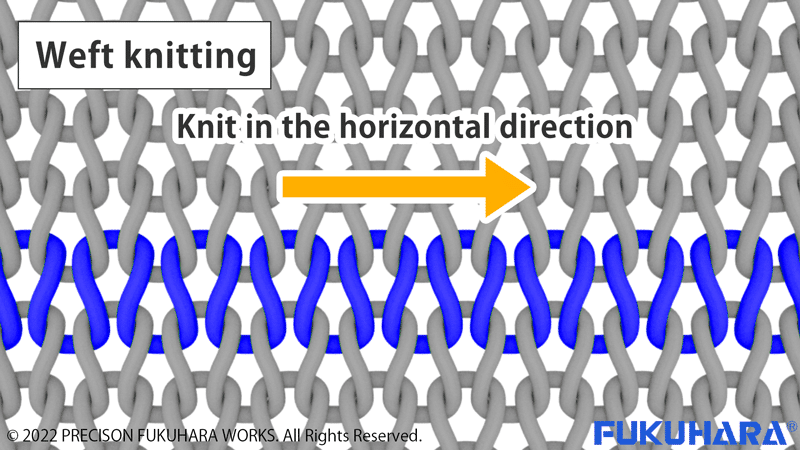
As mentioned above, knitting machines are roughly divided into warp and weft knitting, and weft knitting is further divided into horizontal and circular knitting.In warp knitting, the yarn is continuously knitted vertically while shaking it left and right, while in weft knitting, the yarn is continuously knitted horizontally.
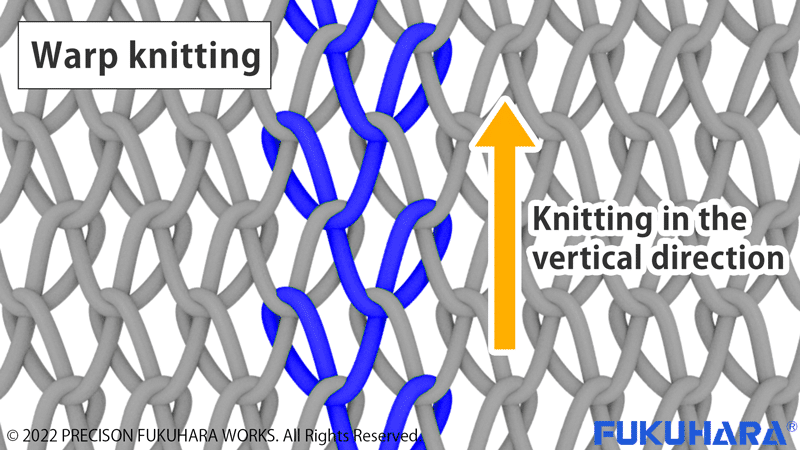
The warp and weft knitting machines are further classified as shown in the figure below, and the circular knitting machine we manufacture is the bench-top circular knitting machine marked with * in the figure. The official name of our circular knitting machines is “table-top circular knitting machines,” but in the industry, they are simply called “circular knitting machines. The official name of the machine is “table-top circular knitting machine,” but in the industry it is simply called a circular knitting machine.
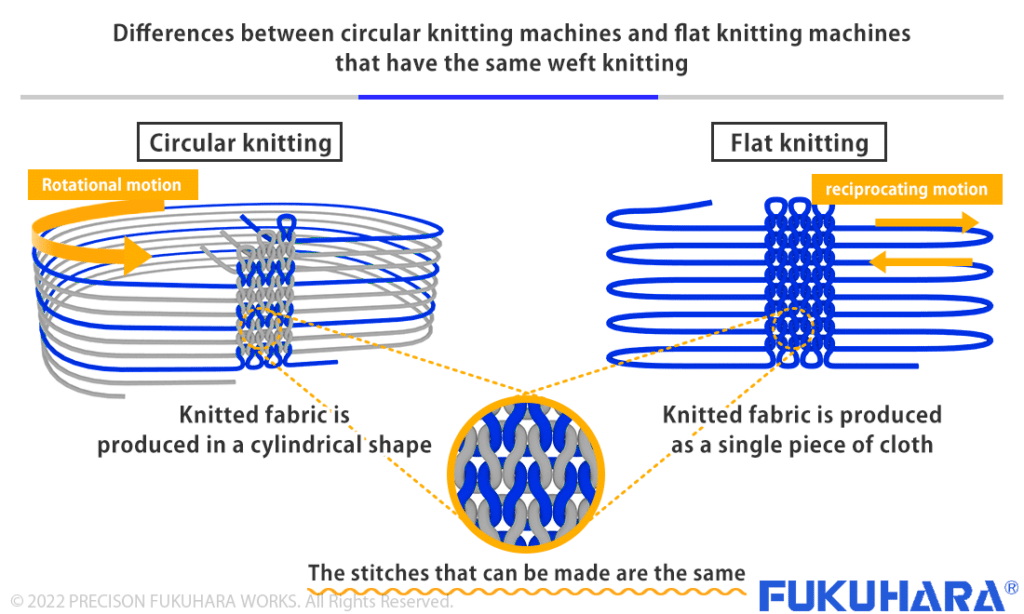
Circular Knitting Machines and Flat Knitting Machines
The difference between a circular knitting machine and a weft knitting machine lies in the production volume, the range of knit size, and the complexity of the knitting structure that can be knitted.
There is an overwhelming difference in the production volume between a flat knitting machine, which basically knits one yarn in a reciprocating motion, and a circular knitting machine, which knits around 100 yarns in a rotating motion at the same time.
There is also a big difference in the range of knit size between circular knitting machines, which have high productivity and can produce a sufficient amount of fabric even with small knitting patterns, and flat knitting machines, which have low productivity.
Gauge is a term used to describe the density of needles in a knitting machine, and it indicates the number of needles per inch (25.4mm). While flat knitting machines are generally between 3 gauge and 21 gauge, our circular knitting machines are between 2 gauge and 60 gauge, which is about three times the gauge range.
While circular knitting machines have an overwhelming advantage in terms of productivity and gauge range, flat knitting machines have an overwhelming advantage in terms of the complexity of the knitting structure.
Therefore, highly fashionable sweaters and knitted products that require complex knitting structures can only be knitted on flat knitting machines.
Main products in which circular knitting machine knitted fabrics are used
clothing

T-shirts

polo shirts

dress shirt

innerwear

Sportswear

sweater

Stretch
jeans
Stretch
suit
(raw) material

eyeglass cloth

Base fabric for poultice

Mattress surface fabric

car seat
The Future of Circular Knitting Machines
As mentioned above, there is a wide range of products that can be made with circular knitting machines, and the products introduced here are just a few examples.
In recent years, there has been a shift from textiles to knitwear, and products that used to be made with textiles, such as jeans, suits, and shirts, are now being made with knitwear.
For example, jeans, suits, and shirts are now made of knitted fabrics.
In addition to mattresses, circular knitted fabrics are used in a variety of other materials, and many new material applications are being explored.
In addition, the use of circular knitting machines, which are much more mobile and productive than other textile machines, can be expected to reduce the size of factories and save energy. Therefore, it is said that a paradigm shift to circular knitting has begun in the world of textiles, as it can contribute to the SDGs, which are currently the focus of global attention.
It is said that a paradigm shift to circular knitting has begun in the world of textiles. The demand for circular knitting machines will continue to grow and advance as the BEST OF TEXTILE MACHINE.
